SpringAI Source
流式对话
Spring AI调用大模型
Spring AI调用大模型的入口:
org.springframework.ai.openai.api.OpenAiApi#chatCompletionStream
public Flux<ChatCompletionChunk> chatCompletionStream(ChatCompletionRequest chatRequest,
MultiValueMap<String, String> additionalHttpHeader) {
Assert.notNull(chatRequest, "The request body can not be null.");
Assert.isTrue(chatRequest.stream(), "Request must set the stream property to true.");
AtomicBoolean isInsideTool = new AtomicBoolean(false);
return this.webClient.post()
.uri(this.completionsPath)
.headers(headers -> headers.addAll(additionalHttpHeader))
.body(Mono.just(chatRequest), ChatCompletionRequest.class)
.retrieve()
.bodyToFlux(String.class)
// cancels the flux stream after the "[DONE]" is received.
.takeUntil(SSE_DONE_PREDICATE)
// filters out the "[DONE]" message.
.filter(SSE_DONE_PREDICATE.negate())
.map(content -> ModelOptionsUtils.jsonToObject(content, ChatCompletionChunk.class))
// Detect is the chunk is part of a streaming function call.
.map(chunk -> {
if (this.chunkMerger.isStreamingToolFunctionCall(chunk)) {
isInsideTool.set(true);
}
return chunk;
})
// Group all chunks belonging to the same function call.
// Flux<ChatCompletionChunk> -> Flux<Flux<ChatCompletionChunk>>
.windowUntil(chunk -> {
if (isInsideTool.get() && this.chunkMerger.isStreamingToolFunctionCallFinish(chunk)) {
isInsideTool.set(false);
return true;
}
return !isInsideTool.get();
})
// Merging the window chunks into a single chunk.
// Reduce the inner Flux<ChatCompletionChunk> window into a single
// Mono<ChatCompletionChunk>,
// Flux<Flux<ChatCompletionChunk>> -> Flux<Mono<ChatCompletionChunk>>
.concatMapIterable(window -> {
Mono<ChatCompletionChunk> monoChunk = window.reduce(
new ChatCompletionChunk(null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null),
(previous, current) -> this.chunkMerger.merge(previous, current));
return List.of(monoChunk);
})
// Flux<Mono<ChatCompletionChunk>> -> Flux<ChatCompletionChunk>
.flatMap(mono -> mono);
}
MCP
发现有哪些tool
spring ai怎么知道,有哪些tool呢?
依赖于ToolCallbackProvider的作用是:
Implementation of ToolCallbackProvider that discovers and provides MCP tools asynchronously from one or more MCP servers.
This class acts as a tool provider for Spring AI, automatically discovering tools from multiple MCP servers and making them available as Spring AI tools. It:
- Connects to MCP servers through async clients
- Lists and retrieves available tools from each server asynchronously
- Creates AsyncMcpToolCallback instances for each discovered tool
- Validates tool names to prevent duplicates across all servers
这个ToolCallbackProvider有以下几个实现类:
AsyncMcpToolCallbackProvider
SyncMcpToolCallbackProvider
AsyncMcpToolCallbackProvider
其中AsyncMcpToolCallbackProvider,构造方法是:
public AsyncMcpToolCallbackProvider(List<McpAsyncClient> mcpClients) {
this((mcpClient, tool) -> true, mcpClients);
}
即:使用MCP客户端列表,创建新的AsyncMcpToolCallbackProvider实例。
还有一个方法:getToolCallbacks
这个getToolCallbacks方法的作用:发现并返回配置的MCP服务器上的所有可用工具。
过程:
从每个MCP服务器异步检索工具列表。
为每个发现的工具创建AsyncMcpToolCallback。
验证所有服务器中没有重复的工具名称。
代码如下:
public ToolCallback[] getToolCallbacks() {
List<ToolCallback> toolCallbackList = new ArrayList<>();
for (McpAsyncClient mcpClient : this.mcpClients) {
ToolCallback[] toolCallbacks = mcpClient.listTools()
.map(response -> response.tools()
.stream()
.filter(tool -> this.toolFilter.test(mcpClient, tool))
.map(tool -> new AsyncMcpToolCallback(mcpClient, tool))
.toArray(ToolCallback[]::new))
.block();
validateToolCallbacks(toolCallbacks);
toolCallbackList.addAll(List.of(toolCallbacks));
}
return toolCallbackList.toArray(new ToolCallback[0]);
}
那上面的AsyncMcpToolCallbackProvider#getToolCallbacks方法,是在哪里被调用的呢?
调用链如下:
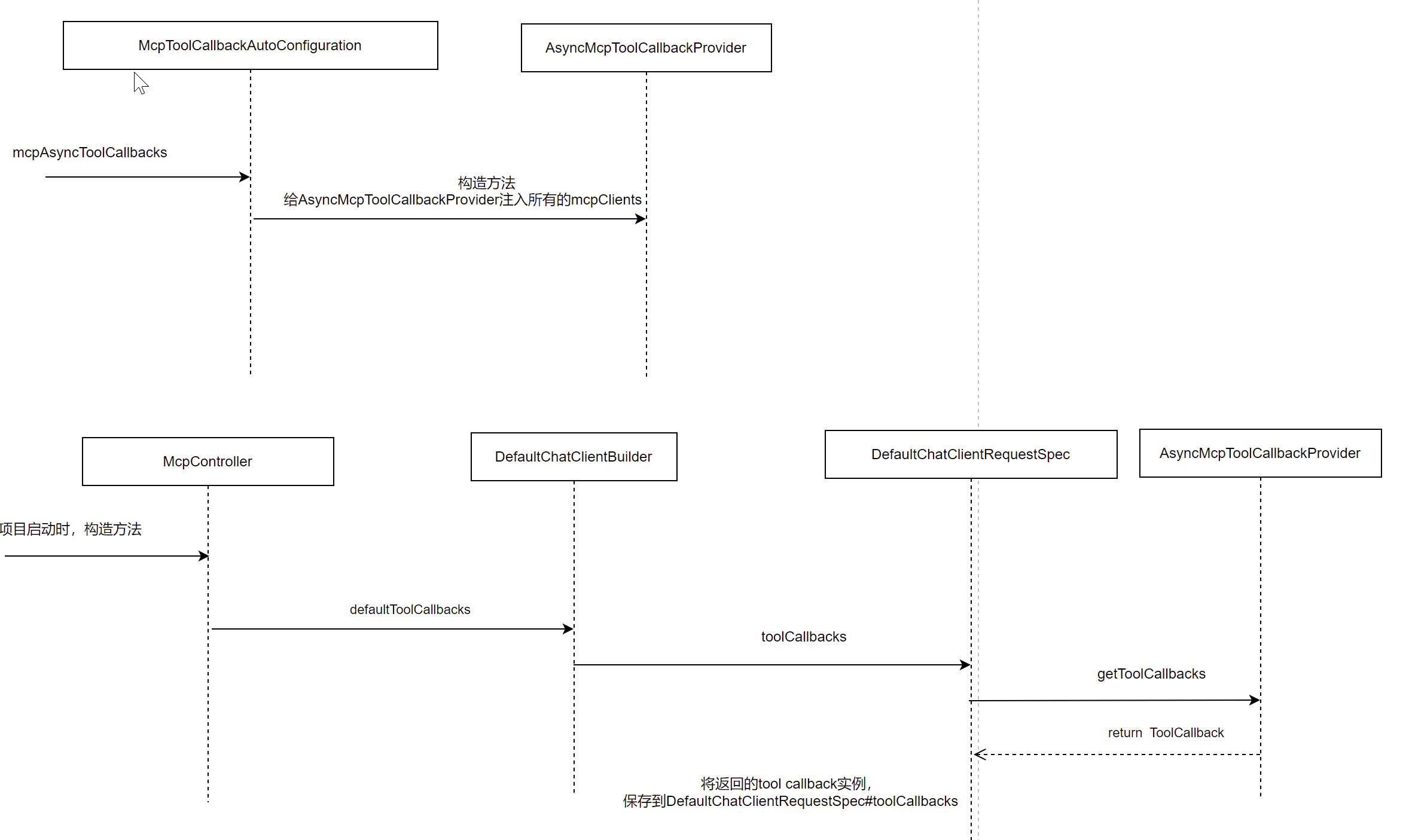
将tool信息,发送给大模型,让大模型判断调用哪个
ChatOptions
主要包含model name、max token 、stop sequence、topK、topP、Temperature等
/**
* Returns the model to use for the chat.
* @return the model to use for the chat
*/
@Nullable
String getModel();
/**
* Returns the frequency penalty to use for the chat.
* @return the frequency penalty to use for the chat
*/
@Nullable
Double getFrequencyPenalty();
/**
* Returns the maximum number of tokens to use for the chat.
* @return the maximum number of tokens to use for the chat
*/
@Nullable
Integer getMaxTokens();
/**
* Returns the presence penalty to use for the chat.
* @return the presence penalty to use for the chat
*/
@Nullable
Double getPresencePenalty();
/**
* Returns the stop sequences to use for the chat.
* @return the stop sequences to use for the chat
*/
@Nullable
List<String> getStopSequences();
/**
* Returns the temperature to use for the chat.
* @return the temperature to use for the chat
*/
@Nullable
Double getTemperature();
/**
* Returns the top K to use for the chat.
* @return the top K to use for the chat
*/
@Nullable
Integer getTopK();
/**
* Returns the top P to use for the chat.
* @return the top P to use for the chat
*/
@Nullable
Double getTopP();
ToolCallingChatOptions
ToolCallingChatOptions 是一个接口,用于配置和管理与聊天模型(ChatModel)交互的选项,包括工具调用(Tool Calling)的设置。这个接口继承自 ChatOptions 接口,因此它也包含了与聊天模型相关的一般配置选项。
主要功能
- 工具回调(ToolCallbacks):
getToolCallbacks():获取注册到ChatModel的工具回调列表。setToolCallbacks(List<ToolCallback> toolCallbacks):设置注册到ChatModel的工具回调列表。
- 工具名称(Tool Names):
getToolNames():获取注册到ChatModel的工具名称集合。setToolNames(Set<String> toolNames):设置注册到ChatModel的工具名称集合。
- 内部工具执行(Internal Tool Execution):
getInternalToolExecutionEnabled():获取是否启用ChatModel负责执行模型请求的工具,或者工具是否应由调用者直接执行。setInternalToolExecutionEnabled(@Nullable Boolean internalToolExecutionEnabled):设置是否启用ChatModel负责执行模型请求的工具。
- 工具上下文(Tool Context):
getToolContext():获取配置的工具上下文。setToolContext(Map<String, Object> toolContext):设置工具上下文值。
- 构建器(Builder):
builder():创建一个新的ToolCallingChatOptions实例的构建器。
ToolCallingChatOptions 接口提供了一种灵活的方式来配置和管理与 ChatModel 交互的选项,特别是与工具调用相关的设置。通过这个接口,开发者可以注册工具回调、设置工具名称、配置工具上下文以及控制工具的执行方式。
Prompt
org.springframework.ai.chat.prompt.Prompt
这个类,由2部分组成:message list 和 chatOptions
其中,message list又分为3部分:
System Text => First in the list
Messages => In the middle of the list
User Test => Last in the list
而chatOptions,就是上面的 ToolCallingChatOptions对象了。
构建ChatClientRequest
构建一个ChatClientRequest,流程如下:
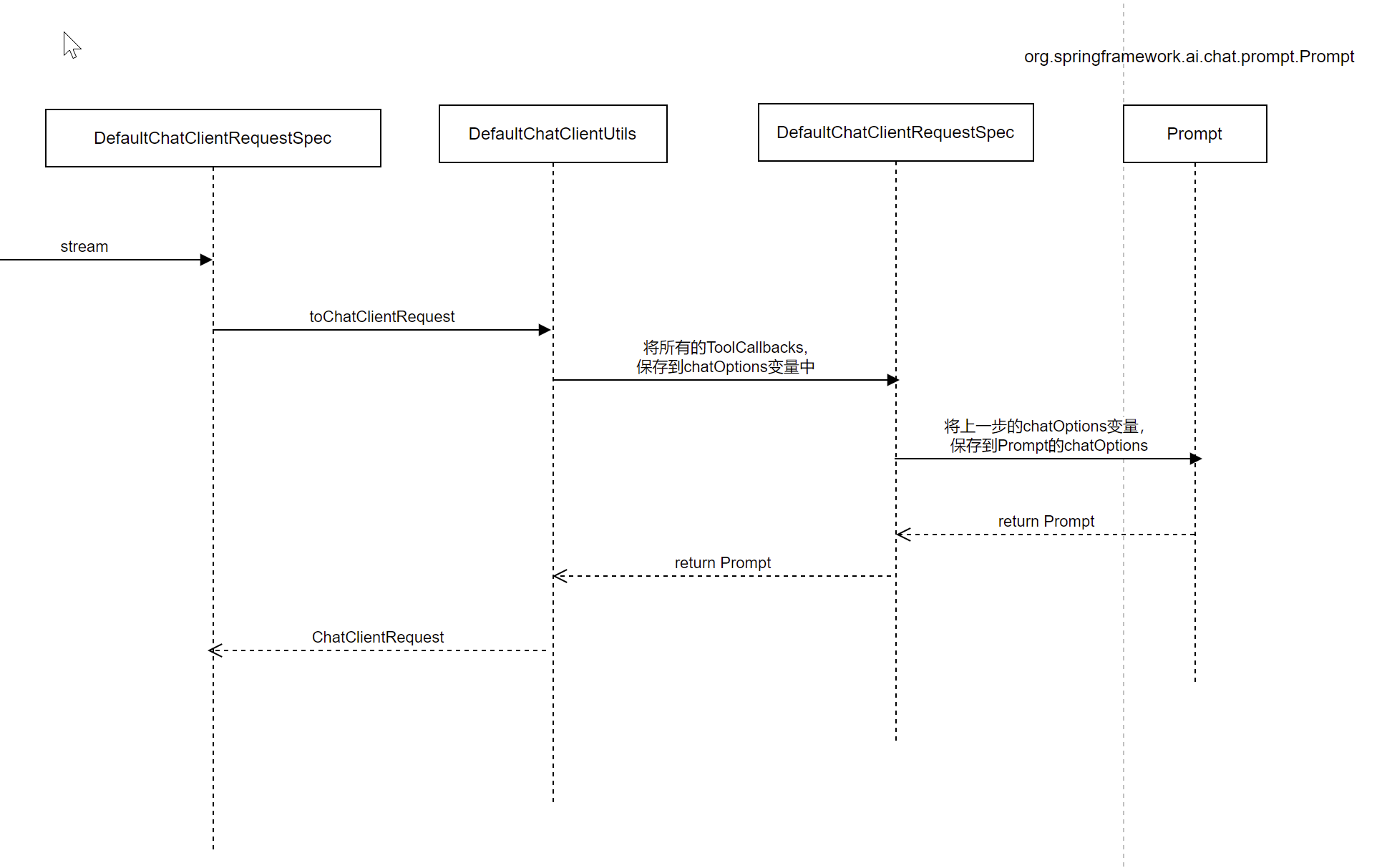
将ChatClientRequest转为ChatCompletionRequest
ChatClientRequest 和 ChatCompletionRequest 是两个不同的类,分别用于表示聊天客户端的请求和与 OpenAI API 交互的请求
转换流程如下:
其实,就是从 ChatClientRequest中,提取出Prompt,然后构建为 ChatCompletionRequest,然后在 OpenAiApi中,发起sse请求LLM,得到大模型的返回值。
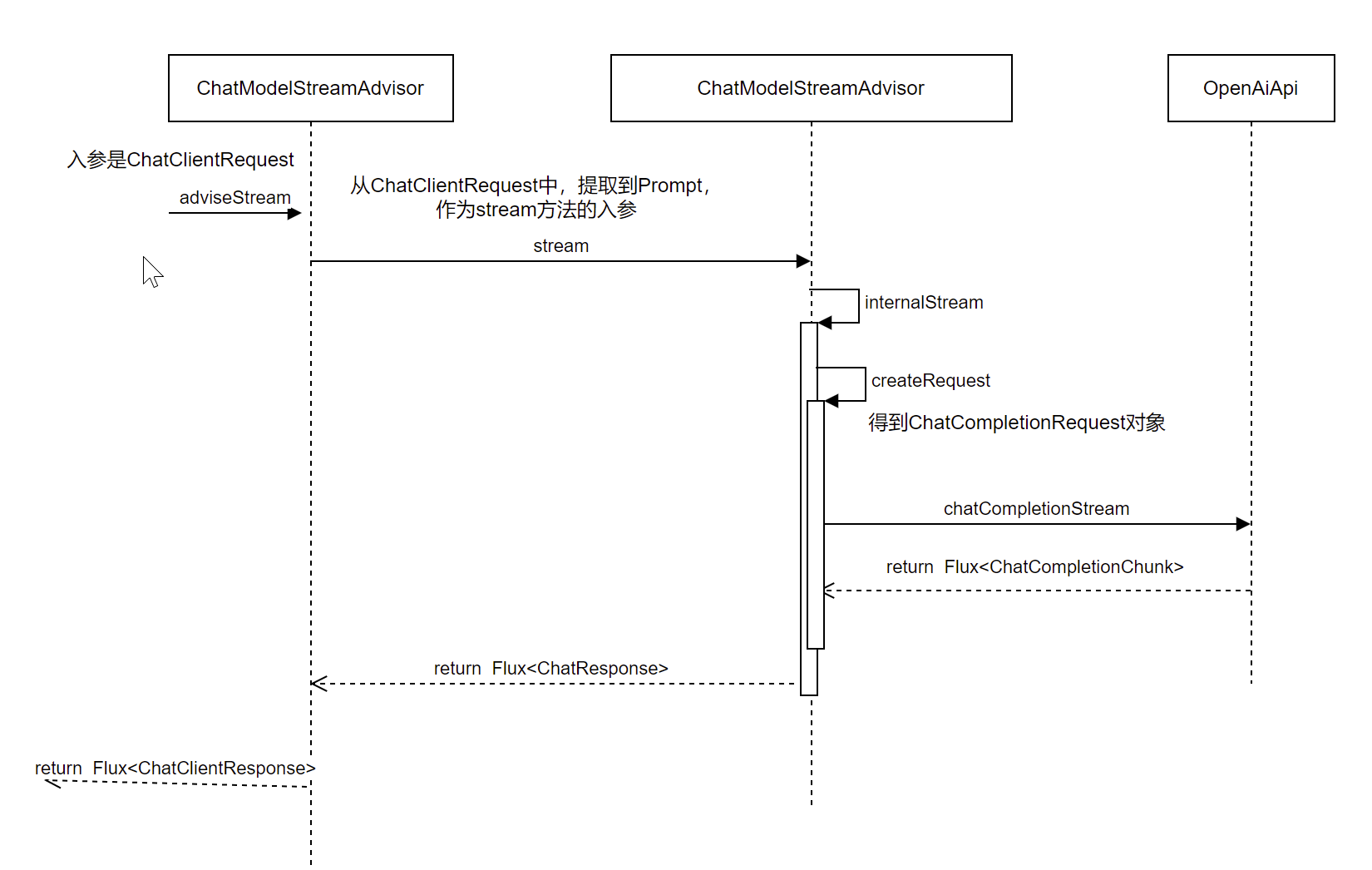
下面,详细描述下,如何将Prompt,构建为 ChatCompletionRequest
// org.springframework.ai.openai.OpenAiChatModel#createRequest
ChatCompletionRequest createRequest(Prompt prompt, boolean stream) {
List<ChatCompletionMessage> chatCompletionMessages = prompt.getInstructions().stream().map(message -> {
if (message.getMessageType() == MessageType.USER || message.getMessageType() == MessageType.SYSTEM) {
Object content = message.getText();
if (message instanceof UserMessage userMessage) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(userMessage.getMedia())) {
List<MediaContent> contentList = new ArrayList<>(List.of(new MediaContent(message.getText())));
contentList.addAll(userMessage.getMedia().stream().map(this::mapToMediaContent).toList());
content = contentList;
}
}
return List.of(new ChatCompletionMessage(content,
ChatCompletionMessage.Role.valueOf(message.getMessageType().name())));
}
else if (message.getMessageType() == MessageType.ASSISTANT) {
var assistantMessage = (AssistantMessage) message;
List<ToolCall> toolCalls = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(assistantMessage.getToolCalls())) {
toolCalls = assistantMessage.getToolCalls().stream().map(toolCall -> {
var function = new ChatCompletionFunction(toolCall.name(), toolCall.arguments());
return new ToolCall(toolCall.id(), toolCall.type(), function);
}).toList();
}
AudioOutput audioOutput = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(assistantMessage.getMedia())) {
Assert.isTrue(assistantMessage.getMedia().size() == 1,
"Only one media content is supported for assistant messages");
audioOutput = new AudioOutput(assistantMessage.getMedia().get(0).getId(), null, null, null);
}
return List.of(new ChatCompletionMessage(assistantMessage.getText(),
ChatCompletionMessage.Role.ASSISTANT, null, null, toolCalls, null, audioOutput, null));
}
else if (message.getMessageType() == MessageType.TOOL) {
ToolResponseMessage toolMessage = (ToolResponseMessage) message;
toolMessage.getResponses()
.forEach(response -> Assert.isTrue(response.id() != null, "ToolResponseMessage must have an id"));
return toolMessage.getResponses()
.stream()
.map(tr -> new ChatCompletionMessage(tr.responseData(), ChatCompletionMessage.Role.TOOL, tr.name(),
tr.id(), null, null, null, null))
.toList();
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported message type: " + message.getMessageType());
}
}).flatMap(List::stream).toList();
ChatCompletionRequest request = new ChatCompletionRequest(chatCompletionMessages, stream);
OpenAiChatOptions requestOptions = (OpenAiChatOptions) prompt.getOptions();
request = ModelOptionsUtils.merge(requestOptions, request, ChatCompletionRequest.class);
// Add the tool definitions to the request's tools parameter.
List<ToolDefinition> toolDefinitions = this.toolCallingManager.resolveToolDefinitions(requestOptions);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(toolDefinitions)) {
request = ModelOptionsUtils.merge(
OpenAiChatOptions.builder().tools(this.getFunctionTools(toolDefinitions)).build(), request,
ChatCompletionRequest.class);
}
// Remove `streamOptions` from the request if it is not a streaming request
if (request.streamOptions() != null && !stream) {
logger.warn("Removing streamOptions from the request as it is not a streaming request!");
request = request.streamOptions(null);
}
return request;
}
文章作者:Administrator
文章链接:http://localhost:8090//archives/springai-source
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议,转载请注明出处!
评论